ISO 12238:2001 pdf download
ISO 12238:2001 pdf download.Pneumatic fluid power一Directional control valves一Measurement of shifting time.
5.3 Pressure transducers
5.3.1 Install a pressure transducer directly into each outlet port to be tested, as well as into the inlet pressure measuring tube.
5.3.2 When a pneumatically-operated valve is tested, mount the control pressure transducer into the pilot pressure measuring tube.
5.3.3 Use pressure transducers, amplifiers and recording devices that together have a system frequency response of within —3,0 dB at 2 000 Hz and a reference time to a known base resolvable to less than 0,1 ms.
5.3.4 Changes in the shifting time caused by limitation of the negative voltage peaks due to the test equipment should not exceed 0,1 ms.
5.4 Supply reservoir
5.4.1 Use a supply reservoir of sufficient capacity so that the pressure drop in the flow tube during the test does not exceed 3 % of the supply pressure. A larger pressure drop is permissible but will increase the shifting time and result in a less favourable rating for the product under test. Connections from the supply reservoir should be several times larger than the pressure measuring tube and as short as possible, to minimize the pressure drop.
5.4.2 Use a supply reservoir that provides for measuring of the internal air temperature of the reservoir.
5.4.3 Locate the optional shut-off valve, and the control valve when applicable, as close as possible to the reservoir outlet. Use a valve whose flow area is larger than that of the pressure measuring tube, because a smaller valve can restrict flow and increase shifting time.
5.5 Control signal
5.5.1 For solenoid pilot-operated valves (see Figure 1), maintain pilot supply pressure at either the pressure supplied to the valve or the maximum rated pilot supply pressure, whichever is less.
5.5.2 For a.c. solenoid-operated valves, generate the control signal with a trigger device set to trigger at the zero voltage crossover point. Maintain voltage to within ± 5 % of the rated voltage.
5.5.3 For d.c. solenoid-operated valves, maintain steady-state voltage to within ± 5 % of the rated voltage.
5.5.4 For pneumatically-operated valves (see Figure 2), maintain the pilot pressure at the same pressure as in the
supply reservoir or at the maximum permitted pilot pressure, whichever is less.
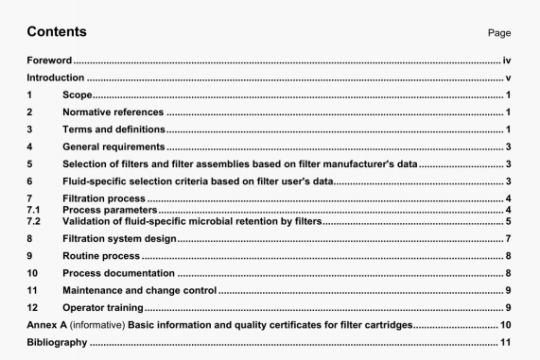
5.6 Data recording system
During a test run, record the pressure variations with time for all transducers in the system. Figure 3 gives examples of how data from an analogue recorder would appear. Other data recording techniques, including digital methods, which do not produce data in this form, may be used.
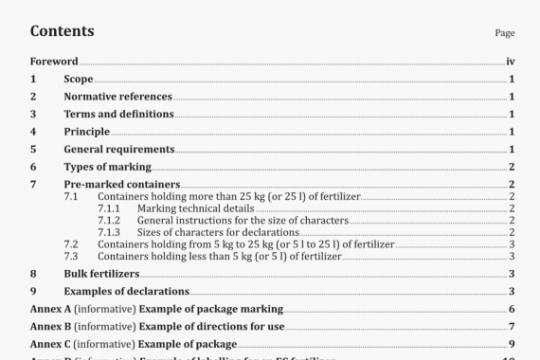
7 Test procedure
7.1 Set up the test circuit as shown in Figure 1 or, when appropriate, Figure 2, with components as specified in
clause 5.
7.2 The fill and exhaust test time for each outlet port shall be measured based on the operation capabilities of the
valve, either shifting on-time or shifting off-time. The following data shall be recorded:
— the fill time from inlet to each outlet port, and
— the exhaust time from each outlet to exhaust port.
Additional data on other possible flow paths through the valve (for example, two inlets for dual pressure valves) may also be recorded.
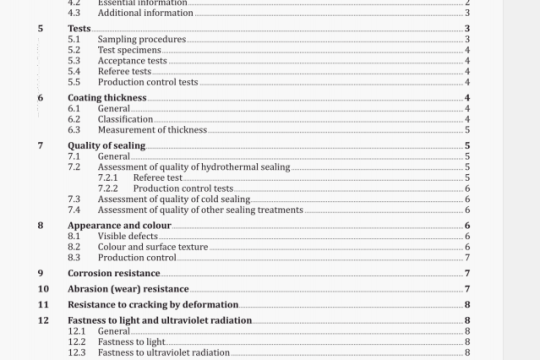
7.3 The fill test time shall be determined as follows.
7.3.1 Maintain supply reservoir pressure at a gauge pressure of 630 kPa (6,3 bar) or at the maximum rated pressure, whichever is less.
7.3.2 Vent the outlet port under test to atmosphere.
7.3.3 Maintain the supply reservoir temperature between 18 °C and 30 °C.
7.3.4 Perform several preliminary valve shifts by energizing or de-energizing the solenoid on electrically-operated valves, or by operating the control valve to pressurize or depressurize the pilot control mechanism on pneumatically- operated valves.
7.3.5 Perform three test runs for each flow path, venting the outlet port each time and waiting at least 1 mm before performing the next test run, to ensure temperature stabilization.
7.4 The exhaust test time shall be determined as follows.
7.4.1 Charge the outlet port under test to a gauge pressure of 630 kPa (6,3 bar) or to the maximum rated pressure, whichever is less.
7.4.2 Maintain the supply reservoir temperature between 18 C and 30 C.
7.4.3 Perform several preliminary valve shifts by energizing or de-energizing the solenoid on electrically-operated valves, or by operating the control valve to pressurize or depressurize the pilot control mechanism on pneumaticallyoperated valves.
7.4.4 Perform three test runs for each flow path, pressurizing the outlet port each time and waiting at least 1 mm before performing the next test run, to ensure temperature stabilization.
7.5 Testing to measure exhaust and fill testing may be combined to run in sequence.